-
1 влияние напряжения питания
влияние напряжения питания
Влияние напряжения питания на функционирование измерительной аппаратуры и, следовательно, на значения измеряемой величины
[ ГОСТ Р 61557-1-2006]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
EN
3.1.39 влияние напряжения питания (effect of the supply voltage): Влияние напряжения питания на функционирование измерительной аппаратуры и, следовательно, на значения измеряемой величины.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 61557-1-2005: Сети электрические распределительные низковольтные напряжением до 1000 В переменного тока и 1500 В постоянного тока. Электробезопасность. Аппаратура для испытания, измерения или контроля средств защиты. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > влияние напряжения питания
-
2 влияние напряжения электропитания
3.29 влияние напряжения электропитания (effect of the supply voltage): Влияние, которое оказывает напряжение электропитания на функционирование измерительной аппаратуры и, следовательно, на результат измерения.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54127-1-2010: Сети электрические распределительные низковольтные напряжением до 1000 В переменного тока и 1500 В постоянного тока. Электробезопасность. Аппаратура для испытания, измерения или контроля средств защиты. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > влияние напряжения электропитания
-
3 линейный нерегулируемый источник электропитания
линейный нерегулируемый источник электропитания
-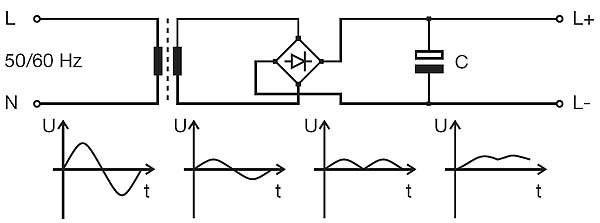
Рис. ABBThe AC mains voltage (50/60 Hz) applied at the input side is transformed to a lower level and rectifi ed by a subsequent rectifi er. Then, a capacitor C smoothes the output voltage of the rectifi er. The dimension of the transformer depends on the desired output voltage.
Due to the design of the electric circuit, the output voltage directly depends on the input voltage which in turn means that variations of the mains voltage have direct effect to the output side. Since no regulation is done on the secondary side, the residual ripple of the output voltage is in the dimension of volts and specifi ed as a percentage of the DC output voltage.
Due to their simple design, unregulated power supplies are very robust and durable. Their effi ciency is approx. 80 %.
Unregulated power supplies are primarily used for simple electromechanical applications that do not require exact output voltages, e.g. for the supply of contactors.
[ABB]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > линейный нерегулируемый источник электропитания
-
4 качество электрической энергии
качество электрической энергии
Степень соответствия параметров электрической энергии их установленным значениям.
[ ГОСТ 23875-88]
качество электрической энергии
КЭ
Степень соответствия характеристик электрической энергии в данной точке электрической системы совокупности нормированных показателей КЭ.
Примечание. Показатели КЭ в некоторых случаях определяют электромагнитную совместимость электрической сети при передаче электрической энергии и приемников электрической энергии, подключенных к данной сети.
[ ГОСТ Р 51317.4.30-2008 (МЭК 61000-4-30:2008)]
качество электроэнергии
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]EN
power quality
characteristics of the electric current, voltage and frequencies at a given point in an electric power system, evaluated against a set of reference technical parameters
NOTE – These parameters might, in some cases, relate to the compatibility between electricity supplied in an electric power system and the loads connected to that electric power system.
[IEV number 617-01-05]
quality of the electricity supply
collective effect of all aspects of performance in the supply of electricity
NOTE – The quality of the electricity supply includes security of electricity supply as a prerequisite, reliability of the electric power system, power quality and customer relationships.
[IEV number 617-01-07]
power quality
characteristics of the electricity at a given point on an electrical system, evaluated against a set of reference technical parameters
NOTE These parameters might, in some cases, relate to the compatibility between electricity supplied on a network and the loads connected to that network.
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]FR
qualité de la tension
caractéristiques du courant, de la tension électrique et de la fréquence en un point donné d’un système d’énergie électrique évaluée selon un ensemble de paramètres techniques de référence
NOTE – Ces paramètres pourraient, dans certains cas, se rapporter à la compatibilité entre l’électricité fournie sur un réseau d’énergie électrique et les charges raccordées à ce réseau d’énergie électrique.
[IEV number 617-01-05]
qualité de la fourniture d’électricité
effet d’ensemble de tous les aspects de performance dans la fourniture d’électricité
NOTE – La qualité de la fourniture d’électricité comprend la sécurité de la fourniture d’électricité en tant que préalable, la fiabilité du réseau d’ énergie électrique, la qualité de la tension et les relations clientèle.
[IEV number 617-01-07]
qualité de l’alimentation
caractéristiques de l’électricité en un point donné d’un réseau d’énergie électrique, évaluée par rapport à un ensemble de paramètres techniques de référence
NOTE Ces paramètres peuvent, dans certains cas, tenir compte de la compatibilité entre l’électricité fournie par un réseau et les charges connectées à ce réseau.
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]Качество электрической энергии (КЭ) определяется совокупностью ее характеристик, при которых электроприемники (ЭП) могут нормально работать и выполнять заложенные в них функции.
КЭ на месте производства не гарантирует ее качества на месте потребления. КЭ до и после включения ЭП в точке его присоединения к электрической сети может быть различно. КЭ характеризуют также термином “электромагнитная совместимость”. Под электромагнитной совместимостью понимают способность ЭП нормально функционировать в его электромагнитной среде (в электрической сети, к которой он присоединен), не создавая недопустимых электромагнитных помех для других ЭП, функционирующих в той же среде.
[В. В. Суднова. Качество электрической энергии]
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Online technology fully isolates and protects against all power quality disturbances.
[APC]Технология ИБП с двойным преобразованием энергии полностью изолирует и защищает нагрузку от любых нарушений качества электроэнергии.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
Близкие понятия
Действия
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
- виновник ухудшения качества электрической энергии
- качество электроэнергии в точке присоединения к электрической сети
- качество электроэнергии на месте потребления
- качество электроэнергии на месте производства
EN
DE
- Elektrizitätsversorgungsqualität, f
- Spannungsqualität, f
- Versorgungsqualität
FR
- qualité de la fourniture d’électricité
- qualité de la tension
- qualité de l’alimentation
- Qualitе du service
Смотри также
1. Качество электрической энергии
D. Versorgungsqualität
E. Quality of supply
F. Qualité du service
Степень соответствия параметров электрической энергии их установленным значениям
Источник: ГОСТ 23875-88: Качество электрической энергии. Термины и определения оригинал документа
3.20 качество электрической энергии (power quality) КЭ: Степень соответствия характеристик электрической энергии в данной точке электрической системы совокупности нормированных показателей КЭ.
Примечание - Показатели КЭ в некоторых случаях определяют электромагнитную совместимость электрической сети при передаче электрической энергии и приемников электрической энергии, подключенных к данной сети.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51317.4.30-2008: Электрическая энергия. Совместимость технических средств электромагнитная. Методы измерений показателей качества электрической энергии оригинал документа
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > качество электрической энергии
5 явление электрической дуги
явление электрической дуги
-
[Интент]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Electric arc phenomenon
The electric arc is a phenomenon which takes place as a consequence of a discharge which occurs when the voltage between two points exceeds the insulating strength limit of the interposed gas; then, in the presence of suitable conditions, a plasma is generated which carries the electric current till the opening of the protective device on the supply side.
Gases, which are good insulating means under normal conditions, may become current conductors in consequence of a change in their chemical-physical properties due to a temperature rise or to other external factors.
To understand how an electrical arc originates, reference can be made to what happens when a circuit opens or closes.
During the opening phase of an electric circuit the contacts of the protective device start to separate thus offering to the current a gradually decreasing section; therefore the current meets growing resistance with a consequent rise in the temperature.
As soon as the contacts start to separate, the voltage applied to the circuit exceeds the dielectric strength of the air, causing its perforation through a discharge.
The high temperature causes the ionization of the surrounding air which keeps the current circulating in the form of electrical arc. Besides thermal ionization, there is also an electron emission from the cathode due to the thermionic effect; the ions formed in the gas due to the very high temperature are accelerated by the electric field, strike the cathode, release energy in the collision thus causing a localized heating which generates electron emission.
The electrical arc lasts till the voltage at its ends supplies the energy sufficient to compensate for the quantity of heat dissipated and to maintain the suitable conditions of temperature. If the arc is elongated and cooled, the conditions necessary for its maintenance lack and it extinguishes.
Analogously, an arc can originate also as a consequence of a short-circuit between phases. A short-circuit is a low impedance connection between two conductors at different voltages.
The conducting element which constitutes the low impedance connection (e.g. a metallic tool forgotten on the busbars inside the enclosure, a wrong wiring or a body of an animal entered inside the enclosure), subject to the difference of potential is passed through by a current of generally high value, depending on the characteristics of the circuit.
The flow of the high fault current causes the overheating of the cables or of the circuit busbars, up to the melting of the conductors of lower section; as soon as the conductor melts, analogous conditions to those present during the circuit opening arise. At that point an arc starts which lasts either till the protective devices intervene or till the conditions necessary for its stability subsist.
The electric arc is characterized by an intense ionization of the gaseous means, by reduced drops of the anodic and cathodic voltage (10 V and 40 V respectively), by high or very high current density in the middle of the column (of the order of 102-103 up to 107 A/cm2), by very high temperatures (thousands of °C) always in the middle of the current column and – in low voltage - by a distance between the ends variable from some microns to some centimeters.
[ABB]Явление электрической дуги
Электрическая дуга между двумя электродами в газе представляет собой физическое явление, возникающее в тот момент, когда напряжения между двумя электродами превышает значение электрической прочности изоляции данного газа.
При наличии подходящих условий образуется плазма, по которой протекает электрический ток. Ток будет протекать до тех пор, пока на стороне электропитания не сработает защитное устройство.
Газы, являющиеся хорошим изолятором, при нормальных условиях, могут стать проводником в результате изменения их физико-химических свойств, которые могут произойти вследствие увеличения температуры или в результате воздействия каких-либо иных внешних факторов.
Для того чтобы понять механизм возникновения электрической дуги, следует рассмотреть, что происходит при размыкании или замыкании электрической цепи.
При размыкании электрической цепи контакты защитного устройства начинают расходиться, в результате чего постепенно уменьшается сечение контактной поверхности, через которую протекает ток.
Сопротивление электрической цепи возрастает, что приводит к увеличению температуры.
Как только контакты начнут отходить один от другого, приложенное напряжение превысит электрическую прочность воздуха, что вызовет электрический пробой.
Высокая температура приведет к ионизации воздуха, которая обеспечит протекание электрического тока по проводнику, представляющему собой электрическую дугу. Кроме термической ионизации молекул воздуха происходит также эмиссия электронов с катода, вызванная термоэлектронным эффектом. Образующиеся под воздействием очень высокой температуры ионы ускоряются в электрическом поле и бомбардируют катод. Высвобождающаяся, в результате столкновения энергия, вызывает локальный нагрев, который, в свою очередь, приводит к эмиссии электронов.
Электрическая дуга длится до тех пор, пока напряжение на ее концах обеспечивает поступление энергии, достаточной для компенсации выделяющегося тепла и для сохранения условий поддержания высокой температуры. Если дуга вытягивается и охлаждается, то условия, необходимые для ее поддержания, исчезают и дуга гаснет.
Аналогичным образом возникает дуга в результате короткого замыкания электрической цепи. Короткое замыкание представляет собой низкоомное соединение двух проводников, находящихся под разными потенциалами.
Проводящий элемент с малым сопротивлением, например, металлический инструмент, забытый на шинах внутри комплектного устройства, ошибка в электромонтаже или тело животного, случайно попавшего в комплектное устройство, может соединить элементы, находящиеся под разными потенциалами, в результате чего через низкоомное соединение потечет электрический ток, значение которого определяется параметрами образовавшейся короткозамкнутой цепи.
Протекание большого тока короткого замыкания вызывает перегрев кабелей или шин, который может привести к расплавлению проводников с меньшим сечением. Как только проводник расплавится, возникает ситуация, аналогичная размыканию электрической цепи. Т. е. в момент размыкания возникает дуга, которая длится либо до срабатывания защитного устройства, либо до тех пор, пока существуют условия, обеспечивающие её стабильность.
Электрическая дуга характеризуется интенсивной ионизацией газов, что приводит к падению анодного и катодного напряжений (на 10 и 40 В соответственно), высокой или очень высокой плотностью тока в середине плазменного шнура (от 102-103 до 107 А/см2), очень высокой температурой (сотни градусов Цельсия) всегда в середине плазменного шнура и низкому падению напряжения при расстоянии между концами дуги от нескольких микрон до нескольких сантиметров.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > явление электрической дуги
6 реле (p) (к)
relay (к)
электромеханическое устройство, контакты которого размыкают и /или замыкают управляемую цепь в зависимости от наличия или величины эл. сигналов в управляющей цепи, — an electromechanical device in which contacts are opened and/or closed by variations in the conditions of one electric circuit and thereby affect the operation of other devices in the same or other electric circuits.
-, арретирующее — latching relay
-, барометрическое (барореле для раскрытия парашюта) — barometric release (mechanism)
-, бесконтактное — contactless relay
- блокировки — blocking relay
-, биметаллическое — bimetallic relay
- блокировки (выключения) — lockout relay
- блокировки (выключения) автомата торможения — anti-skid lockout relay
- блокировки включения систем самолета, двигателя при обжатой передней амортстойке шасси — ground shift relay (actuated with nose oleo compressed)
-, блокировочное — blocking relay
реле, связанное с другими устройствами и, служащее для предотвращения срабатывания ипи повторного включения цепи при нарушении нормальной работы. — a relay wtlich со-operates with other devices to block tripping or to block reclosing on an out-of-step condition. or on power swings.
-, блокировочное — locking-out /lockout/ relay
реле, служащее для выключения оборудования и удержания его в выключенном состоянии при нарушении нормальной работы.данного оборудования, — an electrically operated hand or electrically reset device which functions to shut down and hold an equipment out of service on occurrence of abnormal conditions.
- включения (и выключения) — switching relay
реле, включающее или выключающее к-л. устройство или цепь, — the relay which can place another device or circuit in an operating or nonoperating state.
- включения (одного устройства к другому, напр., преобразователя к шине) — (inverter-to-bus) switching /connection, tie/ relay
- включения муфты стартера — starter meshing relay
- включения наземного питания — external power relay
- включения стартерного pежима (стартера-генератора) — motorizing relay
- времени — time relay
- времени, электромашинное — rotary time-delay relay
-, вызывающее срабатывание системы (цепи) — system /circuit/ actuating relay
-, выключающее — cutout /cut-out/ relay
- выключения (защитного устройства, контактора, оборудования) — tripping relay. used to trip а circuit breaker, contactor, equipment.
- выключения (блокировки оборудования при нарушении нормальных условий работы) — lock-out relay
- выключения зажигания (двиг.) — ignition cut-out relay
-, герметическое — pressure sealed relay
-, гидравлическое (сигнализатор) — hydraulic pressure switch
- давления (сигнализатор давления) — pressure switch
реле, срабатывающее при изменении давления подводимого газа или жидкости — a switch actuated by а change in the pressure of a gas or liquid.
- двухпозиционное (е замыканием контактов в двух крайних положениях) — double-throw relay. а relay which alternately completes а circuit at either of its two extreme positions.
-, двухполюсное — double pole relay
динамического торможения (фотокамеры) — (camera) dynamic braking relay
- дифференциальное — differential relay
реле с несколькими обмотками, которое срабатывает, когда разность величин подводимого напряжения или протекающего тока в обмотках достигает определенного уровня. — a relay with multiple windings that functions when the voltage, current, or power difference between the windings reaches а predetermined value.
-, дифференциально-минимальное (дмр) — differential reverse current cutout relay
- задержки времени — time delay relay
реле, обеспечивающее временной интервал между включением и выключением обмотки и перемещением якоря, — a relay in which there is an appreciable interval of time between the energizing or deenergizing of the coil and the movement of the armature.
-, защитное — protective relay
реле, служащее для защиты цепей в случае нарушения нормального режима работы, — a relay, the principal function оf which is to protect services from interruption or to prevent or limit damage to apparatus.
-, защитное дифференциальнoe — differential protective relay
- защиты от перенапряжения — overvoltage relay
-, командное — control relay
- контроля нагрузки — load monitor relay (lmr)
-, максимальное — overload relay
реле, срабатывающее, если сила тока, протекающего в его обмотке, превышает установленную величину, — a relay designed to operate when its coil current rises above а predetermined value.
- мгновенного действия — instantaneous relay
-, минимальное — reverse current (cut-out) relay
устанавливается в цепи между генератором пост. тока (или выпрямительным устройством) и шиной пост. тока для предотвращения обратного тока в случае, если напряжение на шине превышает выходное напряжение генератора. — reverse current cut-out relays are placed between the dc generator, transformerrectifier, and the dc bus to prevent reverse current flow, if the dc bus potential becomes greater than dc generator or transformerrectifier output.
- на два направления (двухпозиционное) — double-throw relay
- напряжения — voltage relay
реле, срабатывающее при заданной величине подаваемого напряжения, — a relay that functions at а predetermined value of voltage.
- обжатого положения шасси (для включения систем ла) — ground shift mechanism relay
- обратного тока — reverse-current relay
реле, срабатывающее при протекании тока в обратном направлении, — a relay that operates whenever current flows in the reverse direction.
- объединения шин (подсистем лев. и прав. борта) — bus tie relay (btr)
- отключения объединения шин — tie bus isolation relay
- перегрузки (максимальное) — overload relay
- переключения потребителей (pпп) — load monitor relay (lmr)
- переключения стартера-генератора на стартерный режим — motorizing relay
- переключения шин (эл.) — bus tie relay (btr)
- переменного тока — ас operated relay
-, пневматическое (сигнализатор давления) — pneumatic pressure switch
- подает напряжение на... — relay applies voltage to..., relay energizes...
- подает (+27 в) на... — relay applies (+27 v) to..., relay makes /closes/ circuit to supply /apply, feed/ +27 v to...
-, поляризованное — polarized relay
реле, направление перемещения якоря которого зависит от направления тока в его обмотке. — а relay in which the arma'ture movement depends on the direction of the current. its coil symbol is sometimes marked +.
- предельного значения скорости — maximum operating limit speed relay
- предельного значения числa m. — maximum operating limit mach-number relay
-, промежуточное (вспомогательное) — auxiliary relay
- пускового зажигания (двиг.) — starting ignition.relay
-, развязывающее — decoupling relay
-, разделительное — isolation relay
- сигнализатора обледенения — ice detector pressure switch
- сигнализации достижения предельной скорости — maximum operating limit speed (warning) relay
- сигнализации нарушения (параметров) питания — power relay. it may be an overpower or underpower relay.
- сигнализации отказа питания — power fail relay
- с механической блокировкой — latching relay
- соединения шин — bus tie relay (btr)
- с самоблокировкой — interlock relay
реле, в котором один якорь не может изменить свое положение или его обмотка не может оказаться под током, если другой якорь не занимает определенное положение. — a relay in which one armature cannot move or its coil be energized unless the other armature is in a certain position.
-, стопорное (запорное) — latch-in /latching, locking/ relay
реле, контакты которого стопорятся (фиксируются) либо в замкнутом или разомкнутом положении до момента расстопорения вручную или электрически. — а relay with contacts that lock in oither the energized or de-energized position until reset either manually or electrlcally.
- стрельбы — firing control relay, fire relay
- снимает напряжение с... (обесточивает цепь) — relay de-energizes..., relay removes voltage from...
- снимает +27 в с... — rela@ removes +27 v from..., relay breakes /opens/ circuit to remove +27 v from...
- срабатывает (и замыкает цепь) — relay operates (and closes circuit)
- срабатывает и (своими контактами) подает +27 в на клемму 1 — relay operates and applies +27 v to terminal 1
- срабатывает и приводит в действие эл. мотор — relay actuates electric motor
-, струйное
электромагнитное устройство, распределяющее входное давление (воздуха, рабочей жидкости) в двух выходных каналах. — jet relay
-, тепловое — thermal relay
реле, срабатывающее под воздействием нагрева, создаваемого протекаемым током. — а relay (hat responds to the heating effect of an energizing current.
-, управляющее — control relay
-, чувствительное — sensitive relay
-, шаговое — stepping relay
-, электромагнитное — electromagnetic relay
электромагнитный контактор, имеющий обмотку (обмотки) и подвижный якорь, — an electromagnetically operated switch composed of one or more coils and armatures.
-, эпектромашинное — rotary relay
-, электронное — electronic relay
электронная цепь, выполняющая функцию реле, без наличия подвижных деталей. — an electronic circuit that provides the functional equivalent of a relay, but has no moving parts.
отпускание p. (на размыкание контактов) — tripping off
срабатывание р. — operation of relay
включать р. — energize relay
выключать (обесточивать) р. — de-energize relay
переключать(ся) р. — reset relay (manually or electrically)
- притягивать якорь р. — attract relay armature
удерживать р. в заданном положении — hold relay in the given positionРусско-английский сборник авиационно-технических терминов > реле (p) (к)
7 виды коррекции коэффициента мощности
виды коррекции коэффициента мощности
-There are 2 types of power factor correction: fixed or automatic.
Fixed power factor correction consists of inserting, in parallel on the network, a capacitor bank whose total power is provided by the assembly of capacitors of identical or different ratings. The bank is energized by a contactor that simultaneously supplies all the capacitors (a single step).
The inrush current peak, in the case of fixed correction, can reach 30 times the nominal current of the capacitor bank.
An automatic power factor correction system, on the other hand, consists of several capacitor banks of identical or different ratings (several steps), energized separately according to the value of the power factor to be corrected.
An electronic device automatically determines the power of the steps to be energized and activates the relevant contactors.
The inrush current peak, in the case of automatic correction, depends on the power of the steps already on duty, and can reach 100 times the nominal current of the step to be energized.
[ABB]
PFC Types
There are two types of Power Factor Correction - Passive PFC and Active PFC.
Passive PFC uses passive elements like a ferrite core inductor on the AC input. It is very easy to implement in existing power circuits although the power factor is low at 60-80%. The proper AC input voltage (115V or 230V) must also be chosen manually. In addition, significant EMI can still result with a 115V AC source. Of course, a 230V AC source will not have this problem!.
Active PFC, on the other hand, uses a switching regulator with active elements like an IC, FETs (Field Effect Transistors) and diodes to create an active PFC circuit. This circuit allows the power supply to achieve a power factor of up to 95%, significantly reduce harmonics and automatically adjusts the AC input voltage. This means you do not have to manually select the AC input voltage. It works with all voltages from 110V to 240V.
[ http://www.techarp.com/showarticle.aspx?artno=81&pgno=1]
Тематики
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > виды коррекции коэффициента мощности
См. также в других словарях:
Voltage drop — is the reduction in voltage in an electrical circuit between the source and load. In electrical wiring national and local electrical codes may set guidelines for maximum voltage drop allowed in a circuit, to ensure reasonable efficiency of… … Wikipedia
Voltage doubler — A voltage doubler is an electronic circuit which charges capacitors from the input voltage and switches these charges in such a way that, in the ideal case, exactly twice the voltage is produced at the output as at its input. The simplest of… … Wikipedia
The Conduit — Developer(s) High Voltage Software Publisher(s) Sega … Wikipedia
Voltage regulator — A popular three pin 12 V DC voltage regulator IC. A voltage regulator is an electrical regulator designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage level. A voltage regulator may be a simple feed forward design or may include negative feedback … Wikipedia
Control of the National Grid — The National Grid is the high voltage electric power transmission network in Great Britain, connecting power stations and major substations, and has a synchronized organization such that electricity generated anywhere in Great Britain can be used … Wikipedia
Photoelectric effect — The photoelectric effect is a quantum electronic phenomenon in which electrons are emitted from matter after the absorption of energy from electromagnetic radiation such as x rays or visible light.cite book | title = Physics for Scientists… … Wikipedia
Antenna effect — The antenna effect, more formally plasma induced gate oxide damage, is an effect that can potentially cause yield and reliability problems during the manufacture of MOS integrated circuits [ T. Watanabe, Y. Yoshida, “Dielectric Breakdown of Gate… … Wikipedia
Voltage spike — In electrical engineering, spikes are fast, short duration electrical transients in voltage (voltage spikes), current (current spike), or transferred energy (energy spikes) in an electrical circuit.Fast, short duration electrical transients… … Wikipedia
Technological and industrial history of the United States — The technological and industrial history of the United States describes the United States emergence as one of the largest nations in the world as well as the most technologically powerful nation in the world. The availability of land and labor,… … Wikipedia
Power supply — For the Budgie album, see Power Supply (album). A vacuum tube rackmount adjustable power supply, capable of +/ 1500 volts DC, 0 to 100mA output, with amperage limiting capability. A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy … Wikipedia
Switched-mode power supply — switched mode power supply. A bridge rectifier B Input filter capacitors C Transformer D output filter coil E output filter capacitors ] A switched mode power supply, switching mode power supply or SMPS, is an electronic power supply unit (PSU)… … Wikipedia
Перевод: с русского на английский
с английского на русский- С английского на:
- Русский
- С русского на:
- Все языки
- Английский
- Немецкий
- Французский
